728x90
문제
로마 숫자를 int 값으로 바꾸어 반환할 것
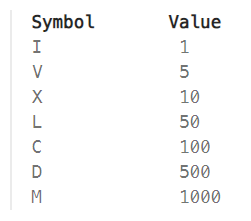
주의할 점
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900.
Example 3:
Input: s = "MCMXCIV" Output: 1994 Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
풀이
첫 시도
class Solution {
String[] special = {"CM", "CD", "XC", "XL", "IX", "IV"};
int[] value1 = {900, 400, 90, 40, 9, 4};
String[] normal = {"M", "D", "C", "L", "X", "V", "I"};
int[] value2 = {1000, 500, 100, 50, 10, 5, 1};
public int romanToInt(String s) {
int cal = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < special.length; i++) {
if (s.contains(special[i])) {
s = s.replace(special[i], "");
cal += value1[i];
}
}
if (!s.isEmpty()) {
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
for (int i = 0; i < normal.length; i++) {
if ((c + "").equals(normal[i])) {
cal += value2[i];
}
}
}
}
return cal;
}
}- 특수 경우인 ["CM", "CD", "XC", "XL, "IX", "IV"] 를 String 배열로 미리 선언 후, 이에 맞는 int 배열을 함께 선언 [900, 400, 90, 40, 9, 4]
- 보통의 경우인 ["M", "D", "C", "L", "X", "V", "I"] 를 String 배열로 미리 선언 후, 이에 맞는 int 배열을 함께 선언 [1000, 500, 100, 50, 10, 5, 1]
- (사실 상 모든 경우의 수를 미리 선언한 것)
- for문을 돌며 특수 경우를 파악한 후, s.replace()를 사용하여 ""(공백)처리한 뒤 값을 cal에 더함
- 위 과정 후 s가 아직 비어있지 않다면 s를 char 배열로 전환하여 보통의 경우를 다시 계산함
- 시간복잡도 : O(N^2) (String의 replace()가 O(N)의 시간복잡도를 가짐)
💬이 방법은 풀이는 가능하지만 너무 복잡하여 다른 풀이를 참조함
풀이 참조 후 재시도
class Solution {
public int romanToInt(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> m = new HashMap<>();
m.put('I', 1);
m.put('V', 5);
m.put('X', 10);
m.put('L', 50);
m.put('C', 100);
m.put('D', 500);
m.put('M', 1000);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (i < s.length() - 1 && m.get(s.charAt(i)) < m.get(s.charAt(i + 1))) {
ans -= m.get(s.charAt(i));
} else {
ans += m.get(s.charAt(i));
}
}
return ans;
}
}- Map을 사용하여 미리 값들을 저장한 후, 앞 뒤 숫자의 크기를 비교하여 더 작은 수가 앞에 와있다면 빼는 식의 계산 방법을 사용한 풀이
- 생각하지 못한 방법이지만 훨씬 효율적인 방법!
- 시간복잡도 : O(N)
'JAVA > Coding Test Study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Easy] LeetCode - no.14 Longest Common Prefix ⭐ : Java (0) | 2024.10.13 |
|---|---|
| [Easy] LeetCode - no.58 Length of Last Word : Java (0) | 2024.10.13 |
| [Easy] LeetCode - no.121 Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock ⭐ : Java (3) | 2024.10.13 |
| [Easy] LeetCode - no.169 Majority Element : Java (0) | 2024.10.13 |
| [Easy] LeetCode - no.26 Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array : Java (0) | 2024.10.13 |